Muses
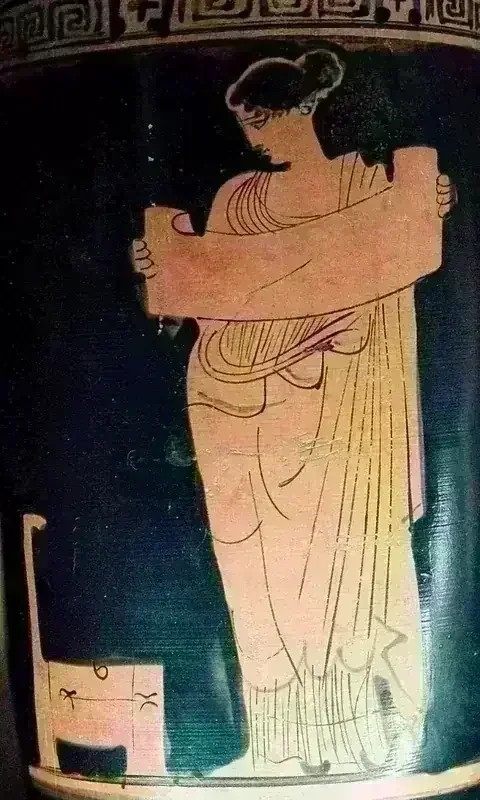

In ancient Greek religion and mythology, the Muses (Ancient Greek: Μοῦσαι, romanized: Moûsai; Modern Greek: Μούσες, romanized: Múses) are the inspirational goddesses of literature, science, and the arts. They were venerated as the divine source of knowledge expressed through poetry, lyric songs, and myths that were transmitted orally for centuries throughout ancient Greek culture. While the number and names of the Muses varied by region in early traditions, the Classical period standardized their number to nine, with their names commonly given as Calliope, Clio, Polyhymnia, Euterpe, Terpsichore, Erato, Melpomene, Thalia, and Urania.
In modern figurative language, the term muse refers to a person who serves as someone's source of artistic inspiration.